Sample data used in this example is the China400.udb datasource. The road, lake, and administrative region data are involved. Query:
- Lakes contained in Hunan province.
- Roads that passes by Hunan province with the road code of G320.
Basic Steps:
- Open the China.udb datasource in the current workspace.
- Create a new map window and add the three datasets ProvincesR, LakeR, and Road_L to the newly created map window.
- In the map window, select the region indicating the Hunnan province in the Provinces_R layer, that is the searching object.
- On the Spatial Analysis tab, in the Query group, click Spatial Query to open the Spatial Query dialog box.
-
Specify the spatial query condition and attribute query condition for the searched layer.
- Click the Spatial Query Condition dropdown button for the RoadL layer in the layer list and select “IntersectRegionLine” to query roads that pass by Hunan.
- Click the Attirbute Query Condition dropdown button for the RoadL layer in the layer list, click “Expression”, and compose the SQL expression RoadL.CODE = “G320” in the dialog box that shows up.
- Click the Spatial Query Condition dropdown button for the LakeR layer in the layer list and select “ContainRegionRegion” to query lakes in Hunan province.
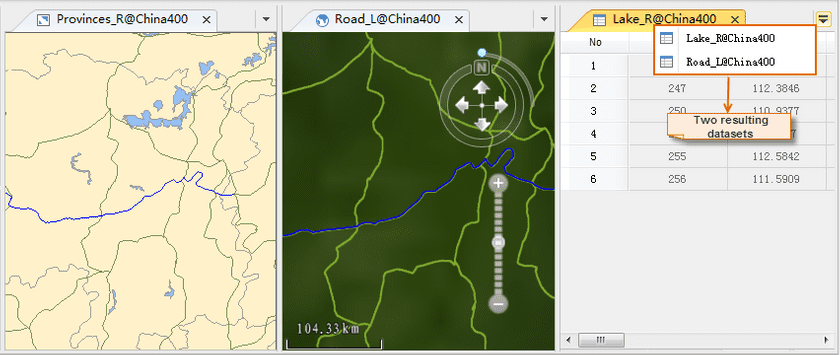
- Select the RoadL and LakeR layers, check the Browse in Attribute Table, Highlight in Map, and Highlight in Scene boxes.
- Select the RoadL, check the Save Results box, specify the target datasource as China.udb, and rename the result dataset as “HunnanRoadG320”.
Similarly, rename the result dataset for the Lake_R layer as “HunanLake”.