To meet the needs of different user groups, provides two methods: interactive query building and writing SQL expressions to build queries, helping you construct SQL Query expressions that meet business requirements.
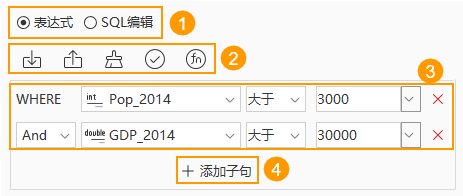
Building Queries Interactively
By using dropdown options, you can quickly specify logical statements, query fields, logical operators, and other elements to build common SQL Query expressions without requiring SQL knowledge.
As shown in the figure below, the interface and steps for interactive query building are as follows:
- Select Expression to build a query.
- Expression management tools, from left to right: Import, Export, Clear, Check expression, function.
- Import: Import an *.xml file containing expression information, and the expression input box below will automatically fill in the corresponding details.
- Export: After setting the expression, you can export it to an *.xml file for reuse.
- Clear: Clear all content in the current expression input box.
- Check expression: Verify the correctness of the expression. Click the check expression button; if correct, it will prompt "Expression correct" below the input box; if incorrect, it will show "Wrong expression".
- function: Organizes function information that may be used in SQL expressions. For details, refer to Function Descriptions for Building SQL Queries.
- Expression input, from left to right: logical statement (Where, And, Or), query field, logical operator, judgment value, delete button.
- Logical statement: The logical word for the first statement is Where, and it cannot be changed. For the second and subsequent statements, the default logical word is And, which can be switched to Or via the dropdown.
- Query field: The default query field is the first field of the dataset and can be selected from the provided dropdown menu.
- Logical operator: The default logical operator is Greater Than, and others can be chosen from the dropdown. The available operators depend on the query type, showing only those applicable to it.
- Judgment value: Enter or select a judgment value via dropdown, which can be a value or a field.
- Delete: If multiple query statements are not needed, you can delete a statement using this button.
- Add clause: When multiple expressions need to be input, click the Add clause button to add a statement input line.
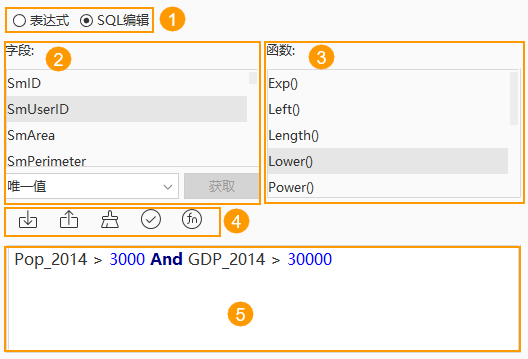
Building Queries by Writing SQL Expressions
If you have a basic understanding of SQL and the search is complex, using SQL expression writing to build queries can more efficiently help you complete the task.
As shown in the figure below, the interface for building queries by writing SQL expressions is explained as follows:
- Switch the SQL expression input method to SQLEdit.
- The field list displays all fields in the dataset; interactive edit operations include:
- Double-click a field to insert it directly into the expression input box.
- After selecting a field, use the Get button to retrieve all its values, shown in the Unique Value dropdown. Select a value to auto-fill it into the input box.
- The function list includes ten common functions; double-click one to insert it into the expression input box.
- Expression management tools, from left to right: Import, Export, Clear, Check expression, function. Usage is consistent with that described in interactive query building.
- The expression input box requires only the "where" clause. For example, if the full SQL expression is "Select * from Province_R where Pop_2014 > 3320 And GDP_2014 > 30000", enter only "Pop_2014 > 3320 And GDP_2014 > 30000". While typing, it auto-suggests fields or logical keywords based on input characters, e.g., typing "o" lists "or" and "order by" keywords and fields starting with "o".
Related Topics
Building SQL Expression Queries
Common Expressions for Building SQL Queries
Function Descriptions for Building SQL Queries



