Donut Polygon
Function Description
A donut polygon is a complex geometry type. In an editable state, two or more polygon objects with inclusion relationships are processed in overlapping areas (deleted or retained; if the number of polygons is even, overlapping parts are removed; if odd, they are retained), ultimately forming a donut polygon. For example, when there is a lake within a region, a donut polygon is obtained.
- Donut polygons are applicable to polygon layers or CAD layers.
- Selecting two or more polygon objects and performing a donut polygon operation can result in the following scenarios:
- If the selected polygon objects do not intersect, a complex object is generated.
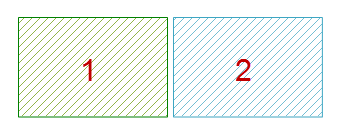
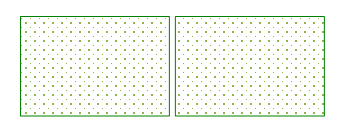
- If the selected polygon objects intersect at points or lines, they are merged into a single complex object.
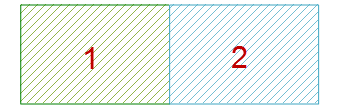
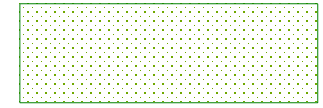
- If the selected polygon objects intersect by area but do not overlap completely, when the polygon object count is odd, the intersecting parts are retained, resulting in a complex object; when the polygon object count is even, the intersecting parts are deleted, resulting in a complex object.
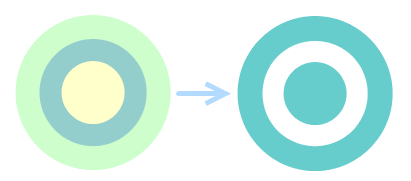
Retain Odd Faces, Delete Even Faces
- If the selected polygon objects completely overlap, when the overlap count is odd, the result is a single polygon object; when the polygon object count is even, all polygon objects are deleted.
Performing a donut polygon operation on three overlapping circles results in one circle object; performing the operation on two overlapping circles results in null.
- If the selected polygon objects do not intersect, a complex object is generated.
Function Entry
- Features Tab -> Feature Editing Group -> Donut Polygon.
- Image Mosaic Tab -> Feature Editing Group -> Donut Polygon.
Operation Instructions
- With the layer editable, select one or more polygon objects.
- In the Gallery control of the Feature Editing group under the Features tab, click the Donut Polygon button to open the Donut Polygon dialog.
In the Donut Polygon dialog, you can set the operation method for each field individually or select multiple fields to configure uniformly. The following describes the dialog.
- Edit Layer: The editable layer dropdown lists all editable layers in the current map. Click the dropdown arrow on the right to select the target layer.
- Field List Area: This area lists all non-system fields and editable system fields in the current editable layer, including field, type, and the operation method for the new object’s field after the connection operation. By default, the field attributes of the first object are used.
- Operation Method Setting Area: Provides four operation methods:
- Null: After the operation, the value of this field in the new object is null.
- Sum: After the operation, the value of this field in the new object is the sum of the corresponding field values from all source operation objects.
- Weighted Mean: After the operation, the value of this field in the new object is the weighted mean of this field from all source objects. A weighting field must be specified. If no weighting field is selected, the simple average is calculated by summing the selected field values of all source objects and dividing by the number of source objects.
- Save Geometry: After the operation, the value of this field in the new object is the same as that of a currently selected object. Click the dropdown arrow on the right to select the object property value to use for the new object.
- Keep Hole: Check this box to save the hole area in the donut polygon operation result as a separate polygon object, making it easier for users to perform other operations and settings on it. As shown below, if the box is unchecked, the hole area has no object and appears blank (left image); after checking the Keep Hole box, the hole area in the result is saved as a polygon object (right image), allowing users to set its style, attributes, etc.
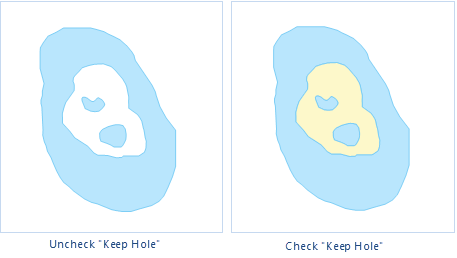
Figure: Donut Polygon Result Comparison
- Click the OK button to complete the donut polygon operation.



